

Vegetable Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Agriculture Sector

Are you about starting a vegetable farm? If YES, here’s a complete sample vegetable farming business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE to raise money .
Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a vegetable farming business. We also took it further by analyzing and drafting a sample vegetable farming marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for vegetable farms. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
Suggested for You
- Marijuana Cultivation Business Plan [Sample Template]
- CBD Hemp Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Lavender Farm Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Soybean Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Rose Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
Why Start a Vegetable Farming Business?
As an aspiring entrepreneur who is interested in starting a business in the agricultural sector of your country, you can be rest assured that there are loads of business opportunities available, and vegetable farming is one of them. Vegetable farming is known to be a profitable business which has over the years evolved from small scale (backyard garden), into a global industry in all countries where it is carried out.
Countries in the Caribbean, South America, North America, Europe, Asia, Australia and Africa are known to be in the forefront when it comes to cultivating varieties of vegetables. If you are considering starting a vegetable farm business, the good news is that you cannot get it wrong.
This is because various types of vegetable are consumed by almost everybody all over the globe. It is important to state that starting a vegetable farming business comes with its own share of challenges, but that does not rule out the fact that it is indeed a profitable business venture.
An aspiring entrepreneur can either choose to start a vegetable farm on a small scale or on a large scale depending on their financial status.
If you have decided to go into vegetable farming, then you should ensure that you carry out thorough feasibility studies and market survey. Business plan is yet another very important business document that you should not take for granted when launching your own vegetable farming business.
Below is a sample vegetable farming business plan template that can help you to successfully write your own with little or no difficulty.
A Sample Vegetable Farming Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Vegetable farmers grow a wide variety of vegetables in open fields and in greenhouses. Some vegetable farmers also grow a variety of fruits and other crops.
If you are a close observer of the vegetable farming industry, you will agree that the industry is anticipated to increase due to increasing consumer health consciousness, which has led to increasing demand for fresh produce. While per capita fruit and vegetable consumption has remained stable in recent time, the price of vegetables has increased as consumers demand premium, fresh vegetables.
So also, the number of both small and large farms has been increasing. Small, local farms are benefiting from the organic, local movement, while large, commercial farms are improving labor efficiency. Going forward, players in the vegetable farming industry will continue to increase revenue generation for their business.
The Vegetable Farming industry is indeed a fast – growing industry that is pretty much active in all countries of the world. As a matter of fact, The Netherlands has some of the largest greenhouses where vegetables are cultivated in the world.
That is the scale of food production in the country so much so that in 2000 alone, greenhouses occupied about 10,526 hectares, or 0.25 percent of the total land area.
The Netherlands has an estimate of 4,000 greenhouse establishments that operate well over 9,000 hectares of greenhouses and employ about 150,000 workers, producing €7.2 billion worth of vegetables, fruit, plants and flowers, some 80% of which are exported.
Statistics has it that in the united states of America alone, there are about 76,459 registered and licensed vegetable farms scattered all across the United States responsible for employing about 317,590 and the industry rakes in a whooping sum of $26 billion annually. The industry is projected to enjoy 2.5 percent annual growth.
One thing is certain when it comes to vegetable farming, if you are able to conduct your market research and feasibility studies before choosing a location for cultivating your vegetable, you are likely not going to struggle to grow the vegetable farming business and also sell your vegetables because there are always food processing companies and consumers out there who are ready to buy from you.
Lastly, with vegetable farming it will pay you not to only cultivate vegetable and sell them for consumption in farm markets to retailers and consumers. You can as well start a complimentary business like vegetable processing plant to package your vegetables to save cost.
The bottom line is that if you have enough farm land (space) and you are interested in maximizing vegetable farming, you are sure going to make huge profits from the business.
2. Executive Summary
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a registered and licensed commercial farm that will be based in the outskirts of Los Angeles, California – United States. We have done our detailed market research and feasibility studies and we were able to secure 25 hectares of land to start our vegetable farm.
We will always leverage on greenhouse farming to cultivate vegetable hence we will construct a structure with walls and roof made essentially of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.
At Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC we will be involved in the cultivation of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress,
Basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries. We will also be involved in greenhouse vegetable production.
In the nearest future, hopefully within the first five years of officially running Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC, we will start our food processing and packaging plant and also start exporting our vegetables to other parts of the world.
This is why aside from the fact that we have secured the required farm land and most of the farming equipment and machines, we have also hired key employees who are currently undergoing training so as to be able to fit into the ideal picture of the 21 st century vegetable farming business workforce that we want to build.
We are in the vegetable farming business because we want to leverage on the vast opportunities available in the agriculture industry to contribute our quota in growing the U.S. economy, in national food production, raw materials production for industries, to export agricultural produce from the United States to other countries and over and above to make profit.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is well positioned to become one of the leading vegetable farms in the United States of America, which is why we have been able to source the best hands and machines to run the business with. We have put process and strategies in place that will help us employ best practices when it comes to vegetable farming in the United States of America.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a Private registered commercial farm that is owned by Johnson Jael and his immediate family members. The company will be fully and single handedly managed by the owner – Johnson Jael and his immediate family members at least for a period of time.
3. Our Products and Services
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a commercial farm that will be cultivating various vegetables via greenhouse farming model and land farming for both the United States’ market and the global market. We are in business to produce both vegetables and fruits in commercial quantities.
We will also ensure that we operate a standard food processing and packaging plant as part of our complimentary services. We are in this line of business to make profit and we will ensure that we do all that is allowed by the law of the United States of America to achieve our business goals and objectives.
These are the areas we will concentrate on in our vegetable farms. If need arises we will definitely add more agriculture produce to our list;
- Cultivation of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
- Vegetable and fruit processing and packaging
- Greenhouse construction, consultancy and advisory services
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our Vision is to become one of the leading vegetable farm brands not just in the United States of America but also on the global stage.
- Our mission statement as a commercial farm is to go into full – time cultivation of vegetables and fruits that will not only be consumed in the United States of America but also exported to other parts of the world.
- We want our processed fruits and vegetable to flood the nooks and crannies of the United States and other countries of the world.
Our Business Structure
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a commercial vegetable farm that intends starting small in Los Angeles – California, but hopes to grow big in order to compete favorably with leading commercial vegetable farms in the commercial farming industry both in the United States and on a global stage.
We are aware of the importance of building a solid business structure that can support the picture of the kind of world class business we want to own, which is why we are committed to only hire the best hands in and around California.
At Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC, we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, dedicated, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all our stakeholders (the owners, workforce, and customers).
In view of the above, Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Operating Officer
General Farm Manager
Administrator/Accountant
- Crop (Vegetable and Fruits) Cultivation Manager/Supervisor
Vegetable and Fruits Processing and Packaging Plant Manager/Supervisor
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results; developing incentives; developing a climate for offering information and opinions; providing educational opportunities
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Responsible for the planning, management and coordinating all farm activities across the various sections on behalf of the organization
- Supervises other section manager
- Ensures compliance during project executions (especially in the construction of greenhouse and hothouse et al)
- Providing advice on the management of farming activities across all section
- Responsible for carrying out risk assessment
- Using IT systems and software to keep track of people and progress of the growth of crops
- Responsible for overseeing the accounting, costing and sale of farm produce after harvest
- Represent the organization’s interest at various stakeholders’ meetings
- Ensures that farming goals are achieved, the most efficient resources (manpower, equipment, tools and chemicals et al) are utilized and different interests involved are satisfied. Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Handles all financial transactions for the company
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily farming activities across the various farming sections
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Serves as internal auditor for the company
Crop (Vegetable and fruits) Cultivation Manager/Supervisor
- Responsible for the cultivation of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
- Supervises other workers within the department
- Work closely with the General Manager to achieve the organizations’ goals and objectives
- Responsible for managing the fruits and vegetable processing and packaging plant section of the business
Sales and Marketing Officer
- Identify, prioritize and reach out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of relevant projects.
- Writing winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with company policy
- Responsible for handling business research, marker surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with customers
- Develop, execute and evaluate new plans for expanding increase sales
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the farm
Front Desk/Customer’s Service Officer
- Welcomes guests and clients to the farm by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the company’s products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients
- Receives parcels/documents for Hankins Jordan® Banana Farms, Inc.
- Distribute mails in Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC
- Handles any other duties as assigned by the line manager
6. SWOT Analysis
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC do not intend to launch out with trial and error hence the need to conduct a proper SWOT analysis.
We know that if we get it right from the onset, we would have succeeded in creating the foundation that will help us build a standard vegetable farm that will favorably compete with leading commercial vegetable farms in the United States of America and in other parts of the world.
We are quite aware that there are several large, medium and small scale vegetable farms all over Los Angeles – California and even in the same location where we intend locating ours, which is why we are following the due process of establishing a business.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be welled equipped to confront our threats.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in the commercial farming industry to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives.
Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Hankins Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC;
Our strength as a vegetable farm company is in the fact that we have healthy relationships with loads of major players (agriculture merchants) in the agricultural industry; both suppliers and buyers within and outside of the United States.
We have some of the latest vegetable farming machines, tools and equipment that will help us cultivate crops (vegetables and fruits) in commercial quantities with less stress. Asides from our relationship (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we have some the most experienced hands in the vegetable cum greenhouse commercial farming line of business.
Our major weakness is that we are a new vegetable farm in the United States and it might take some time for our organization to break into the market and gain acceptance especially from international markets in the already saturated and highly competitive commercial farming industry. Another weakness is that we may not have the required cash to promote our business the way we would want to.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities that are available to us cannot be quantified; we know that everybody on planet earth eats different types of vegetables. So also changes in consumer preferences have led supermarkets and other retail outlets to demand fresh vegetables and fruits all year-round. We are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that is available in the industry.
Both the number of small local farms and the number of larger commercial farms have been growing. Increasing imports of fresh produce will slightly constrain demand for vegetables and fruits. Just like any other business, one of the major threats that we are likely to face is economic downturn.
It is a fact that economic downturn affects purchasing/spending power. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new vegetable farm or commercial greenhouse farm in the same location where our target market exists and who may want to adopt the same business model like us.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
If you are conversant with rising technology and scientific development in the agriculture industry, you will quite agree that vegetable and fruits farming via greenhouse commercial farming model are at the front burner. Greenhouse commercial farming is rapidly gaining entrance in our world today.
Greenhouse farming gives room for greater control over the growing environment of various crops. Dependent upon the technicality and specification of a greenhouse design, some of the important factors which may be controlled include temperature, levels of light and shade, irrigation, fertilizer application, atmospheric humidity et al.
Basically, greenhouses are used to overcome shortcomings in the growing qualities of a piece of land such as a short growing season or poor light levels. In essence, they are designed to improve food production in marginal environments.
So also, if you are a close observer of the trends in the vegetable farming industry, you will agree that the vegetable farming industry is anticipated to increase due to increasing consumer health consciousness, which has led to increasing demand for fresh produce.
While per capita fruit and vegetable consumption has remained stable in recent time, the price of vegetables has increased as consumers demand premium, fresh vegetables.
So also, the number of both small and large farms has been increasing; small local farms are benefiting from the organic, local movement while large, commercial farms are improving labor efficiency. Going forward, players in the vegetable farming industry will continue to increase revenue generation for their business.
8. Our Target Market
Naturally, the end consumers of vegetable farm produce and those who benefit from the business value chain of the vegetable farm industry is all encompassing. Every household consumes produce from vegetable farms be it vegetables or fruits et al. In essence, a vegetable farmer should be able to sell his or her farm produce to as many people as possible.
We will ensure that we position our business to attract consumers of fresh vegetables and fruits not just in the United States of America alone but other parts of the world which is why we will be exporting some of our vegetables and fruits either in raw or processed form to other countries of the world.
Our competitive advantage
It is easier to find entrepreneurs flocking towards an industry that is known to generate consistent income which is why there are more commercial farmers in the United States of America and of course in most parts of the world.
For example, Statistics has it that there are 2.2 million farms in the United States of America, covering an area of 922 million acres. This goes to show that there is an appreciable number of farmers in the United States of America but that does not mean that there is stiff competition in the industry.
As a matter of fact, entrepreneurs are encouraged by the government to embrace commercial farming. This is so because part of the success of any nation is her ability to cultivate her own food and also export foods to other nations of the world.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is fully aware that there are competitions when it comes to selling vegetables and fruits all over the globe, which is why we decided to carry out thorough research so as to know how to take advantage of the available market in the United States and in other parts of the world.
We have done our homework and we have been able to highlight some factors that will give us competitive advantage in the marketplace; some of the factors are effective and reliable farming processes that can help us sell our produce at competitive prices, good network and excellent relationship management.
Our competitive advantage lies in the power of our team; our workforce. We have a team of hardworking and highly proficient farmers, a team with excellent qualifications and experience in various niche areas in the vegetable farming industry.
Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected team members, we have some of the latest and efficient vegetable and greenhouse farm machines and equipment and we will be guided by best practices in the industry.
Another competitive advantage that we are bringing to the industry is the fact that we have designed our business in such a way that we will operate an all – round standard vegetable farm that will be involved in diverse areas such as vegetable and fruit cultivation, food processing and packaging plant. With this, we will be able to take advantage of all the available opportunities within the industry.
Lastly, all our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry. It will enable them to be more than willing to build the business with us, help deliver our set goals and achieve all our business aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is in the vegetable farming business for the purpose of maximizing profits hence we have decided to explore all the available opportunities within the industry to achieve our corporate goals and objectives.
In essence we are not going to rely only on the sale of our farm produce to generate income for the business. Below are the sources we intend exploring to generate income for Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC;
- Sale of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
10. Sales Forecast
From the survey conducted, we were able to discover that the sales generated by a vegetable farm depend on the size of the farm and the nature of the vegetable farm.
We have perfected our sales and marketing strategies and we are quite optimistic that we will meet or even surpass our set sales target of generating enough income/profits from the first year of operation and build the business from survival to sustainability.
We have been able to critically examine the vegetable farming industry, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast.
- First Year-: $250,000
- Second Year-: $500,000
- Third Year-: $900,000
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (draughts, epidemics), and unfavorable government policies . Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are quite aware that the reason why some vegetable farms hardly make good profits is their inability to sell off their farm produce, especially perishable crops as at when due. In view of that, we decided to set up a standard food processing plant to help us
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to stakeholders in the agriculture industry, companies that rely on the agriculture industry for their raw materials, supermarkets, grocery stores, hotels and restaurants and agriculture produce merchants et al.
- Advertise our business and agriculture produce in agro – allied and food related magazines and websites
- List our vegetable farms on yellow pages ads
- Attend related agriculture and food expos, seminars and business fairs et al
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Engage in direct marketing
- Encourage the use of Word of mouth marketing (referrals)
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Any business that wants to grow beyond the corner of the street or the city they are operating from must be ready and willing to utilize every available means (conventional and non – conventional means) to advertise and promote the business.
We intend growing our business which is why we have perfected plans to build our brand via every available means. Below are the platforms we can leverage on to boost our vegetable farm brand and to promote and advertise our business;
- Place adverts on both print (newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community based events/programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook, twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our business
- Install our BillBoards on strategic locations all around Los Angeles – California
- Engage in roadshows from time to time in targeted neighborhoods
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas
- Contact corporate organizations and residents in our target areas by calling them up and informing them of Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC and the farm produce we sell
- List our vegetable farms in local directories/yellow pages
- Advertise our vegetable farms in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site.
- Ensure that all our staff members wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles and trucks are well branded with our company logo et al.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
If you want to get the right pricing for your farm produce, then you should ensure that you choose a good location for vegetable farm, choose a good breed/seed that will guarantee bountiful harvest, cut the cost of running your farm to the barest minimum and of course try as much as possible to attract buyers to your farm as against taking your farm produce to the market to source for buyers; with this, you would have successfully eliminate the cost of transporting the goods to the market and other logistics.
We are quite aware that one of the easiest means of penetrating the market and acquiring loads of customers for all our vegetables and fruits is to sell them at competitive prices hence we will do all we can to ensure that the prices of our farm produce are going to be what other commercial farmers would look towards beating.
One thing is certain, the nature of vegetable farming makes it possible for farmers to place prices for their farm produces based on their discretion without following the benchmark in the industry. The truth is that it is one of the means of avoiding running into a loss. The easier you sell off your harvest the better for your business.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our clients make payment for farm produces without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials to clients who may want to deposit cash or make online transfers.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
When it comes to calculating the cost of starting a vegetable farm with a standard greenhouse farm, there are some key factors that should serve as a guide. The most important expenses is the construction of the greenhouse or hothouse as the case may be.
As a matter of fact, if you choose to start mechanized crop farming, then you should be willing to raise huge capital base to start the business. This is so because some cultivation machines/equipment can be pretty expensive. Below are some of the basic areas we will spend our start – up capital in setting up our vegetable farm;
- The total fee for incorporating the business in United States of America – $750
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) at a total premium – $9,400
- The amount needed to acquire/lease a farm land – $50,000
- The amount required for preparing the farm land – $70,000
- The cost for acquiring the required working tools and equipment/machines/fencing et al – $10,000
- The amount required for the purchase of the first set of vegetables and fruits seedlings et al – $50,000
- The amount required to set up a standard vegetable processing plant within the farm facility – $100,000
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $40,000
- The cost of launching an official website – $600
- The amount required for payment of workers for a period of 3 months – $100,000
- Additional Expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,000
Going by the report from detailed research and feasibility studies conducted, we will need an average of $500,000 to start a standard vegetable farm with a processing plant in the United States of America. Basically, vegetable farms do not require an office space, most people that run vegetable farms operate directly from their farms. But we have decided to open a small liaison office; a place where administrative jobs will be carried out.
Generating Funds/Startup Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC
No matter how fantastic your business idea might be, if you don’t have the required money to finance the business, the business might not become a reality. Finance is a very important factor when it comes to starting a vegetable farm. No doubt raising startup capital for a business might not come cheap, but it is a task that an entrepreneur must go through.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a family business that will be owned and managed by Johnson Jael and his immediate family members. They are the sole financiers of the firm but may likely welcome other partners later which is why they decided to restrict sourcing of start-up capital for the business to just three major sources.
- Generate part of the start – up capital from personal savings and sale of his stocks
- Generate part of the start – up capital from friends and other extended family members
- Generate a larger chunk of the startup capital from the bank (loan facility).
N.B: We have been able to generate about $100,000 ( Personal savings $80,000 and soft loan from family members $20,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $400,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to sell our farm produce (vegetables and fruits) a little cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are well prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner of our business strategy.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more as determined by the board of the organization. We know that if this is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry and they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List / Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts in various banks in the United States: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of All form of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of farm land in Los Angeles – California (preparing the farm land inclusive): Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Start – up Capital generation: Completed
- Writing of Business Plan : Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging, Marketing/Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Building /construction of greenhouse and hothouse facility: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed working tools, machines and equipment: Completed
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Farm land Treatment, Health and Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with key players in the industry (agriculture farm produce merchants, transporters/haulage and suppliers of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides): Completed
Need a consultation? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Strategic Planning
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa
- Innovator Founder Visa
- UK Start-Up Visa
- UK Expansion Worker Visa
- Manitoba MPNP Visa
- Start-Up Visa
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa
- Self-Employed Visa
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream
- LMIA Owner Operator
- ICT Work Permit
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA)
- Online Boutique
- Mobile Application
- Food Delivery
- Real Estate
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- Business Valuation
- How it works
- Business Plan Templates
Vegetable Farming Business Plan
Published Mar.29, 2024
Updated Oct.04, 2024
By: Alex Silensky
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 5
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
As explained in our farm business plan example , vegetable farming is booming. More and more people are becoming aware of the benefits of eating fresh vegetables for their health, environment, and society. According to Statista , the global vegetable market can reach $1.08 trillion in revenue in 2024, with an expected annual growth rate of 6.89% from 2024-2028.
Starting a successful vegetable farming business requires appropriate planning, investment, knowledge, and marketing. Without proper foresight, new farmers face pitfalls like investing too much upfront, failing to find customers, or getting overwhelmed by the workload.
This vegetable farming business plan sample helps you:
- Tackle challenges,
- Explore benefits,
- Assess market potential,
- Identify business models and
- Create a targeted marketing plan for your vegetable farm.
By the end, you will have a business plan for vegetable farming tailored to your unique situation.
Challenges of the Vegetable Farming Industry
Starting a vegetable farming business involves four main challenges: high initial investment, seasonal and climatic factors, market fluctuations and competition, and regulatory and environmental issues. Here is how you can deal with each challenge:
1. High Initial Investment
As explained in our fruit and vegetable business plan , starting a farming business requires significant capital. According to a report by Starter Story, the average startup costs for a vegetable farm in 2024 are $19,815. Primary startup costs for starting a vegetable farm include:
- Land acquisition or leasing
- Equipment (tractors, tillers, irrigation systems, etc.)
- Seeds and seedlings
- Fertilizers and pesticides
- Labor costs
- Licensing and permits
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Packaging and transportation costs
- Storage facilities
Tips to reduce initial investment for a vegetable farming business:
- Start small and expand gradually.
- Consider leasing or sharing equipment.
- Explore financing options or grants.
- Invest in cost-effective technology.
- Collaborate with other farms for bulk purchases.
- Optimize resource usage to reduce expenses.
- Focus on high-yield crops for better returns.
- Develop a vegetable growing business plan for financial guidance.
2. Seasonal and Climatic Factors
Vegetable farming is highly dependent on the weather and the seasons. Farms facing failures due to seasonal and climatic factors are a growing concern, particularly with the impacts of climate change.
Tips to adapt to seasonal and climatic factors for a vegetable farming business:
- Rotate and diversify crops.
- Use greenhouses for year-round production.
- Monitor weather forecasts regularly.
- Utilize row covers or frost protection methods.
- Focus on planting and harvesting resilient crops.
- Stay informed on climate change.
- Have contingency plans for extreme weather events.
3. Market Fluctuations and Competition
The vegetable farming industry is very competitive and dynamic. The competition can come from other farmers with lower production costs, higher quality standards, or better marketing strategies.
Tips to overcome market fluctuations and competition challenges in a vegetable farming business:
- Diversify produce to meet market demands.
- Build direct relationships with local markets.
- Use technology for forecasting and planning.
- Engage in farmers’ markets or CSA programs.
- Emphasize quality to stand out.
- Offer unique or specialty crops.
- Collaborate for collective marketing.
- Adapt production to market trends.

4. Regulatory and Environmental Issues
A vegetable farming business is subject to various laws and regulations that govern the quality, safety, and sustainability of vegetable products and practices. Some of these regulations include:
- Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)
- Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA)
- Clean Water Act (CWA)
- Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA)
- Soil Conservation and Domestic Allotment Act
- Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA)
Tips to address the regulatory and environmental issues in a vegetable farming business:
- Research local regulations and obtain necessary permits.
- Develop a sustainability plan, like a garlic farm business plan for eco-friendly farming.
- Implement effective waste management strategies.
- Adopt sustainable farming practices to minimize environmental impact.
- Stay updated on evolving laws.
- Collaborate with agencies for guidance.
- Regularly assess and mitigate environmental risks.
- Train staff on compliance and best environmental practices.
The Benefits of a Vegetable Farming Business
Despite the challenges, vegetable farming offers a unique business opportunity with stable demand, diverse income streams, and scalability. Profit margins often range from 20-35%. The benefits of starting a vegetable farming business include:
1. Financial Benefits
- High profit margins.
- Comparatively lower initial investments.
- Ability to scale and expand to meet demand year-round.
- Multiple pricing models – D2C, restaurants, processed goods, etc.
- Eligible for agriculture subsidies, grants, and financial incentives.
- Vertically integrated with value-added products to maximize revenues.
2. Market Benefits
- Constant and growing consumer demand for fresh vegetables.
- Less susceptibility to market volatility compared to commodity field crops.
- Year-round production capabilities with greenhouse infrastructure.
- Ability to capitalize on the increasing popularity of plant-based diets and locally grown food.
- Direct marketing opportunities through farm-stands, farmers markets, CSAs, etc.
3. Operational Benefits
- Shorter crop cycles and ability to diversify crops throughout the seasons.
- Lower equipment costs compared to commodity crop operations.
- Adaptable to smaller land holdings in peri-urban areas.
- Farm labor is readily available compared to field crops.
- Lower regulatory barriers to entry compared to livestock or cash crops.
Healthy profit margins, diversified income streams, increased market demand, and access to growing niche markets make produce production a promising business model. Crafting a business plan for an E2 visa can also be beneficial if you plan to expand your farming business internationally.
Immigration business plan
The value of vegetable farming market.
The vegetable farming market is large and diverse, with various segments and niches. According to a report by The Business Research Company, the global vegetable farming industry market is expected to grow from $1.65 trillion in 2023 to $1.76 trillion in 2024 at a CAGR of 6.5%. It’s projected to reach $2.17 trillion in 2028 at a CAGR of 5.4%.
The major factors driving the growth of the vegetable farming industry include:
- Population growth
- Health and wellness trends
- Urbanization
- Changing dietary patterns
- Government policies
- Climate change impact
- Global trade dynamics
- Consumer preferences
- Supply chain resilience
- Water scarcity concerns
The major markets for farming are Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America, and South America, with China, India, Nigeria, the Dominican Republic, and the US being the top five producers of vegetables, according to the World Population Review.
Business Opportunities in the Vegetable Farming Business
There are several business opportunities to capitalize on increasing consumer demand for fresh, local produce. Here are some of the top opportunities in the farming sector:
1. Organic Vegetable Farming
What Is Organic Vegetable Farming? Organic vegetable farming involves cultivating vegetables without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. Instead, it relies on natural methods to maintain soil fertility and control pests. Check our organic farming business plan to learn more.
Ideal For – Environmentally conscious producers seeking nutritious and chemical-free produce.
Organic Vegetable Farming Business Plan
- Research organic farming practices.
- Identify suitable land for cultivation.
- Obtain organic certification.
- Cultivate a variety of in-demand produce.
- Establish partnerships with local markets.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand for organic produce.
- Potential for premium pricing.
- Access to niche markets like farmers’ markets and organic grocery stores.
Challenges:
- Higher production costs compared to conventional farming.
- Compliance with organic certification standards.
2. Hydroponic Vegetable Farming
What Is Hydroponic Vegetable Farming? Hydroponic vegetable farming is growing plants in a soilless system where nutrient-rich water solutions deliver essential minerals directly to the roots.
Ideal for – Urban areas with limited space, regions with water scarcity, and individuals interested in high-tech agriculture.
Hydroponic Vegetable Farming Business Plan
- Select suitable hydroponic systems (e.g., NFT, DWC).
- Source quality seeds and nutrient solutions.
- Establish a distribution network targeting local markets or restaurants.
- Invest in technology for climate control and monitoring.
- Ensure proper training for staff on hydroponic techniques.
- Efficient water usage.
- Year-round production.
- High initial setup costs for equipment and technology.
- Technical expertise is required for managing hydroponic systems.
3. Vertical Vegetable Farming
What Is Vertical Vegetable Farming? Vertical vegetable farming involves growing produce in vertically stacked layers or vertically inclined surfaces. This innovative approach maximizes space utilization by taking farming to new heights.
Ideal For – Urban dwellers, restaurants, and communities with limited space but a growing demand for fresh, locally grown produce.
Vertical Vegetable Farming Business Plan
- Select a suitable vertical farming system (e.g., tower gardens, hydroponic towers).
- Choose high-yield crop varieties that thrive in vertical setups.
- Optimize lighting and irrigation systems for efficient growth.
- Establish partnerships with local markets or restaurants for direct sales.
- Implement sustainable practices for resource efficiency.
- Maximizing space utilization for increased yields.
- Providing fresh produce locally year-round.
- Catering to the growing demand for sustainable agriculture practices.
- Initial setup costs are significant.
- High energy consumption.
- Limited crop varieties compared to traditional outdoor farming.
4. Value-added Vegetable Farming
What Is Value-Added Vegetable Farming? Value-added vegetable farming involves processing and enhancing the value of raw produce through methods like canning, pickling, or creating gourmet products. This adds convenience and uniqueness to the product.
Ideal For – Farmers looking to diversify their product offerings, cater to consumer preferences for convenience, and capitalize on the artisanal food trend.
Value-added Vegetable Farming Business Plan
- Identify popular value-added products.
- Source high-quality produce for processing.
- Develop unique recipes and packaging to differentiate products.
- Establish distribution channels through farmers’ markets, specialty stores, and online platforms.
- Maintain strict quality control and food safety standards.
- Allows monetization of surplus or lower-grade fresh produce.
- Offers products with longer shelf life.
- Captures higher margins.
- Additional investments in kitchen equipment and facilities.
- Licensing requirements for processed food production.
- Market competition from large food manufacturers.
Marketing Plan for a Vegetable Farming Business Plan
A marketing plan section of a state farm business plan outlines the strategies and actions that a business will use to achieve its marketing goals and objectives. If seeking funding, a pitch deck services provider can help create a compelling presentation to attract investors.
A marketing plan for a small vegetable farm business plan should include:
Target Market
Competitive analysis, marketing strategies.
- Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Plan
- Sales Forecast
Marketing Budget
Here’s a marketing plan section from a sample vegetable farming business plan of a business called ABC Farms:
Our target markets include:
- Local Restaurants
- Farmers Markets
- Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) Members
- Grocery Stores
- Schools and Cafeterias
- Food Cooperatives
- Health-conscious consumers
Our main competitors are the large-scale conventional producers. Our competitive advantage is our commitment to sustainable practices, focus on soil health, and fresh, high-quality produce.
Marketing Objectives
- Increase brand awareness by 20%
- Expand customer base by 15%
- Increase direct-to-consumer sales revenue by $10,000
- Establish 5 new partnerships
- Achieve a 25% sales increase for new organic products
- Boost social media engagement by 30%
- Participate in 3 events monthly
- Social media marketing
- Email marketing campaigns
- Hosting farm tours and workshops
- Partnership with local restaurants or grocery stores for sourcing
- Participating in farmers’ markets and food festivals
- Implementing a customer loyalty program
- Offering seasonal promotions and discounts
As per our vegetable production business plan, our annual marketing budget is $20,000, which will be allocated as per the chart below:

Our promotion will focus on our organic practices, product freshness, and status as a local farm supporting the community. These qualities help attract consumers.
Partner With OGSCapital for Your Vegetable Farming Business Plan
At OGSCapital, we have the experience and expertise to help you start a successful vegetable farm. We are a team of leading business plan writers with over 17 years of experience and 5,000+ satisfied customers across 42+ industries. Additionally, we provide guidance on documents like the EB2 business necessity letter sample , which can support visa applications for business expansion.
Here are some of the reasons why you should choose us for your business plan for vegetable farm:
- We make custom, high-quality, user-friendly business plans for your goals and needs. For example, our FPO business plan template.
- Our experts are from top B-schools with 15+ years of industry experience. We can boost your business position and investor appeal.
- We use reliable research to give you current and relevant data and insights into the industry.
- We connect you with our network of investors. We have helped our clients raise over $2.7 billion in funding.
Contact us today if you are ready to start your vegetable farm or garden business plan.
Download Vegetable Farming Business Plan Template in PDF
Frequently Asked Questions
How profitable is vegetable farming?
US vegetable farmers’ profits vary widely. Mid-Atlantic direct-market farms earned below $18,500, less than Pennsylvania’s poverty line for two people. But bigger and more diverse farms made more than the median household income in 12 years. US vegetable farms’ profit margins are usually 10-20% of revenue.
What are the best vegetables for farming?
Low-growing greens vegetables like lettuces, spinach, arugula, bok choy, and kale are generally easy to grow and can be successful in various conditions. Other high-income crops for small or backyard growers include strawberries, garlic, and specialty vegetables like heirloom tomatoes and exotic herbs.
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rated document, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
- Agriculture Farming
- Livestock Farming
Project Reports
- Hydroponics
- Best Fertilizers
- Vertical Farming
- Sheep Farming
- Goat Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Fish Farming
- Pig Farming
- Dairy Farming
- Rabbit Farming
- Success Stories of Farmers
- Boost Fruit Yield
- District Wise Crop Production
- Schemes & Subsidies
- Agriculture Colleges
- Farm Insurance
- Disease Control And Management
Agriculture
Aquaculture
Horticulture
Agri Business
Vegetable Farming Business Plan for High Yield and Profits
Table of contents, things to consider in starting a vegetable farming business, production factors and techniques for vegetable farming business, marketing strategies used in a small vegetable farming business plan , importance of vegetable production, factors that determine successful vegetable production, production techniques of quality vegetables, production plan of a vegetable farming business, some of the important high yield vegetable crops, the conclusion of a vegetable farming business plan.
Introduction to vegetable farming business plan
Vegetables are very important sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants providing human health benefits. Vegetable farming business is a profitable business and this not only for a big farmer. It is also profitable for small and marginal farmers. A small-scale vegetable farming has the earning potential throughout the year. If you are planning for commercial vegetable production for maximum profits, you must have a proper vegetable farming business plan.
A step by step guide to vegetable farming business plan
Growing vegetable crops is the perfect way to turn your gardening skills and knowledge into extra income. Business planning is the key to success when you’re ready to invest in starting a vegetable-production business . Poor management and lack of planning are, in many cases, the main causes of business failure. Vegetable farming is a type of crop production intended mainly for human consumption of the crop’s edible parts such as the shoot, leaves, fruits, and roots. According to the consuming part of the crop, vegetables are mainly divided into the following groups;
- Leafy vegetables (lettuce, cabbage, spinach)
- Fruit vegetables (pepper, cucumber, tomato)
- Root vegetables (carrot, radish, sweet potato)
- Bulb vegetables (garlic, onion, fennel)
- Flower vegetables (artichoke, cauliflower, broccoli)
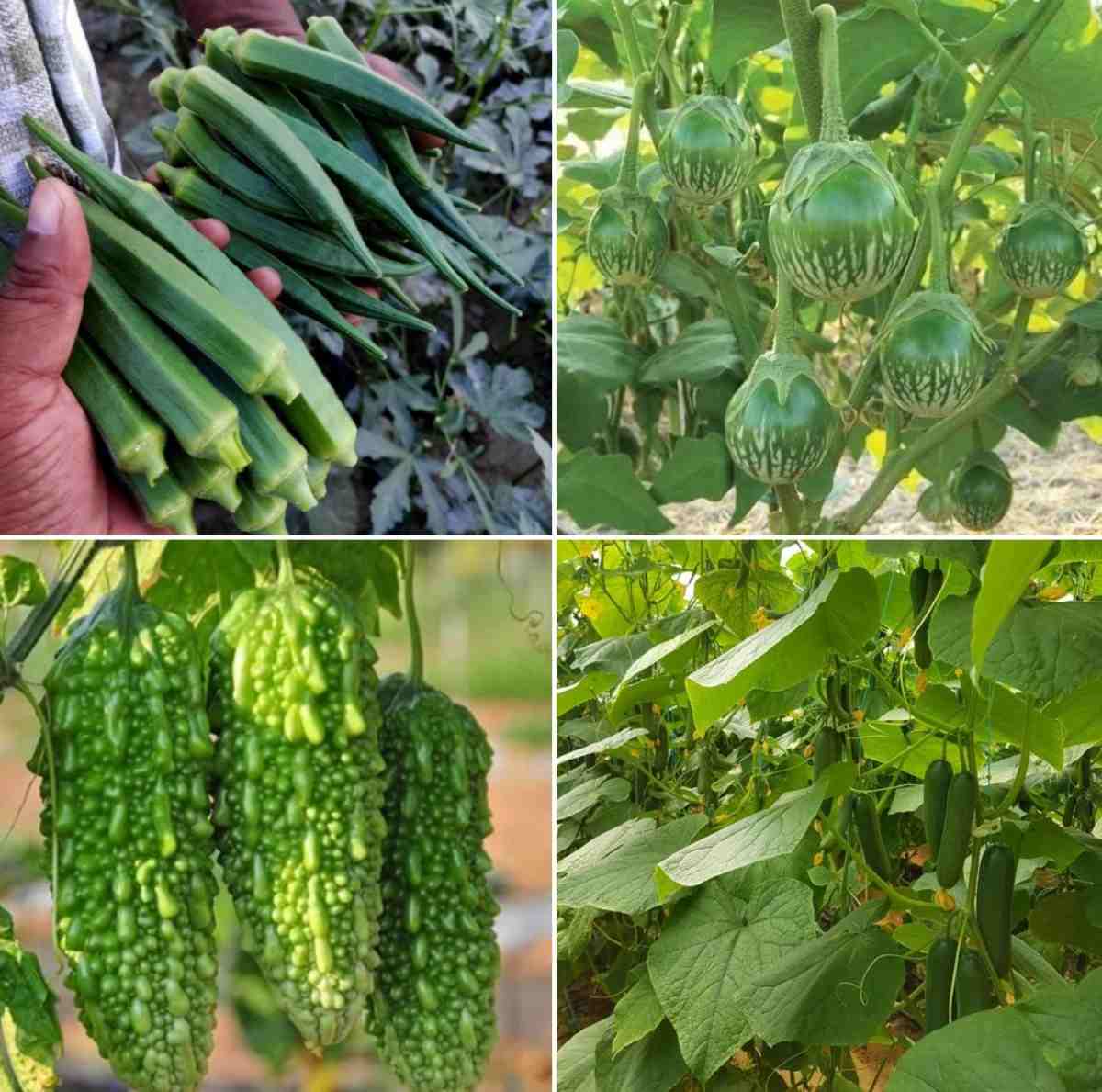

Vegetable farming business demands proper planning, investment, adequate knowledge, and marketing. However, here we have discussed some of the main essentials;
- First of all, a solid vegetable farming business plan is very important.
- In starting, figure out how must land area you have for vegetable farming.
- According to the agro-climatic condition choose the vegetable for farming.
- You must consider the local market because vegetables are hugely perishable items.
- Also, cultivate the scope of export.
- Select the right species.
- Furthermore, you must arrange the proper irrigation for your vegetable farm.
- Plan for harvesting storage.
- Calculate the entire working capital cost.
- Finally, you must arrange the required finance.
Vegetable farming business requires attention to all production operations, including insect, disease, and weed control and efficient marketing. The kind of vegetable grown is determined by consumer demands, which can be defined in terms of vegetable variety, size, tenderness, flavor, and type of pack. Though, effective management involves the adoption of methods resulting in a steady flow of the desired amount of produce over the whole of the natural growing season of the vegetable crop. Many vegetable plants can be grown throughout the year in some climates, while yield per acre for a given kind of vegetable varies based on the growing season and region where the crop is produced.
Climate – Climate involves the temperature level, moisture, daylight, and wind conditions of a specific region. Climatic factors strongly affect all stages and processes of vegetable plant growth
Temperature – Temperature requirements are mainly based on the minimum, optimum, and maximum temperatures during both day and night throughout plant growth.
Moisture – The amount and annual distribution of rainfall in a region, particularly during certain periods of development, affects local crops.
Daylight – Light is the source of energy for vegetable plants. The response of plants to light is mainly dependent upon light intensity, quality, and daily duration.
Site – The choice of a site involves such factors as soil and climatic regions.
Soil preparation and management – Soil preparation and management for vegetable growing involves many of the usual operations required for other crops. Good drainage is important for early vegetables because of wet soil retards development.
Propagation – Propagation of vegetable plants, involving the formation and development of new individuals in the establishment of new plantings, is accomplished by the use of either seeds or the vegetative parts of plants.
Planting – Vegetable crops are planted in the field where they are to grow to maturity. A few kinds are commonly started in a seedbed, established in the greenhouse or the open, and transplanted as seedlings.
Cultivation – Vegetable cultivation refers to stirring the soil between rows of vegetable plants.
Irrigation – Vegetable farming requires irrigation in arid and semi-arid regions, and irrigation is frequently used as insurance against drought in more humid regions.
Disease and insect control – The vegetable production of satisfactory crops requires rigorous disease- and insect-control measures. Crop yield can be lowered by disease or insect attack, and when plants are attacked at an early stage of growth the entire crop may be lost. Reduction in the quality of crops may also be caused by diseases and insects.
Harvesting – The development stage of vegetables when harvested affects the quality of the product reaching the consumer.
Marketing strategy to the small vegetable growing farmer can be;
- Collective approaches, no individual side marketing
- Growing quality vegetables.
- Collection through cooperative or committee.
- Standardization of the product.
- Sale in the outlet by cooperative or Malls.
- Welfare strategy for farmers in profit distribution.
- Government subsidy to the collective approach.
In case if you miss this: Growing Medicinal Plants Hydroponically .

Vegetables are vital to the general good health of human beings, and providing necessary vitamins and minerals, and reducing risk from dangerous diseases and other medical conditions. First, of course, you would need a piece of land to start vegetable farming and try at least an acre for commercial vegetable growing. Then you would require equipment, which you can buy, lease or borrow, such as a tractor, tiller, plow, disc, cultivator, and planter. Lower your production cost as much as possible by spending on equipment only when required. Unnecessary expenses on equipment can eat away potential profits.
Vegetable production provides a promising economic opportunity for reducing rural poverty and unemployment in developing countries and is the main component of farm diversification strategies. Vegetables are mankind’s most affordable source of vitamins and minerals required for good health.
Importance of vegetable production is;
- Importance in human nutrition
- Vegetables are a very important source of farm income
- Vegetables have aesthetic value
- Vegetable production for medicinal purpose
- Roll of vegetables in the national economy
- Flexibility in plant production program-unlike the fruits with vegetables the production program can be adjusted and changed for better profits according to needs. With fruits, it is a difficult time taking and expensive to change the production program if it turns out to be unprofitable.
Whether the growth of vegetables is intended for fresh consumption, processing, and seed production, it can be a profitable vegetable business . However, there are a few factors that can influence the profitability of vegetable production from its early beginnings;
- Seed quality; the sowing of quality, clean, labeled, graded to size, viable, and healthy seed can make all the difference between success and failure in vegetable farming.
- Optimal time of sowing and planting; depends on the climate and environmental conditions of the specific area, as well as requirements of each crop.
- Method of planting; the secret to successful vegetable farming lies in the managing of optimal plant requirements, by combining the production of transplants in the greenhouses with planting in the field.
- Finally, considering effective farm management is the first step in creating profitable vegetable production . In essence, farming of these colorful plants can be a profitable business.
- Some plants have high labor requirements to grow. Before selecting a vegetable to raise, know first the extent at which some plants need tending. Then, determine whether you have the time to invest to grow and market it. For example, if you expect to be unable to get your products sold immediately, avoid easily perishable crops such as asparagus, sweet corn, peas and grow potatoes and onions instead.
- Some plants are difficult to grow and need special attention from the farmer for optimum results. Your choice of the crop must consider whether you have the knowledge and experience in growing such crops and whether you are willing to learn from available resources. Also, some plants would need special equipment. Select those you won’t need to buy the equipment to grow.
You should not miss this: Chilli Seed Germination, Time, Temperature, Procedure .

The quality of vegetables mainly depends on the horticultural production systems, environmental factors, and management practices used. Climatic conditions such as temperature and light intensity have a strong influence on the nutritional quality of vegetables. Hydroponic cultivation technique ensures the production of quality vegetables, and in this culture system, both plant nutrition and environmental conditions are artificially managed according to the plant need. Growing quality vegetables is easier and safer in hydroponic compared to conventional soil culture. The advantages of this system are that plant roots are visible and the root zone environment can be easily monitored. In this system of cultivation, the yield of the vegetable crop can be maximized through the efficient use of all resources, and it is believed to be the intensive form of agricultural enterprises for commercial production of greenhouse vegetable plants .
Soilless culture of vegetables uses inert organic or inorganic substrate through the hydroponic nutrient application. This culture has been reported to practice in the greenhouse as an alternative to conventional filed cultivation of many high-value vegetable crops. Under these protected cultivation systems, weather factors, the amount and composition of nutrient solution, and the growing medium can be managed successfully. Therefore, the quality of vegetable crops grown through soilless culture improves significantly compared to conventional soil culture. Many researchers found better taste, uniformity, color, texture, and higher nutritional value in fruits grown in soilless culture than in soil cultivation methods.
Once you have a clear idea of what you want your vegetable farm business to look like, what you want to produce, and where you will sell your product, you need to establish a production plan. Some factors to consider are listed below;
Capital needs – Identify the investment and cash operating needs and how much you will need to borrow.
Infrastructure and equipment – Identify what equipment you need for the vegetable crops you will produce. Also, depending on the packaging and also handling requirements identify what type of infrastructure will be needed.
Management – Identify the production, management, and marketing skills essential to make your enterprise successful. If you do not have those skills, identify ways to acquire them, which can include hiring additional labor.
Planting and harvesting schedule – Plan the best timing for planting and harvesting your vegetable crops, based on plant varieties and availability of labor. Remember to plan planting dates based on your harvest schedule (e.g., customer demand).
Post-harvest and sanitation – Post-harvesting needs (sanitation, handling, and cooling) are very important aspects that need careful thought. Cooling is essential to delay produce spoilage and keep it fresh. When the product is not sold and delivered immediately after harvest, a cold storage option can be needed.
Enterprise analysis – Keep good plant production and financial records to help you make good decisions in the future. Use records to identify problems that need to be solved and to identify what practices and crops are profitable for your business.
List of high yield vegetable crops can be given below;
Cucumbers – In an acre area, around 12000 cucumber plants are planted (3 plants per square meter) and each plant yields an average of about 5 to 7 kg per cycle. This will yield about 8,400 to 10,500 plants per acre.
Squash – In general, each squash plant produces about 5 to 25 pounds of yellow squash during the growing season. A 10-foot row of yellow squash averages about 20 to 80 pounds of squash.
Beans – The average yield is about 100 to 120 quintals of green pods per hectare can be expected.
Tomatoes – The average tomato crop yield per acre in India is 10 tonnes although the yield varies from 15 to 20 tonnes per acre in case of irrigated crops.
Peanuts – Grown mainly through age-old farming techniques, peanut yield in India is about 700 to 900 kg per hectares.
Potatoes – During the first year of cultivating potatoes, a good yield can be about 10 tons per acre. Experienced farmers after years of practice can achieve yields 16 to 28 tons per acre.
Peppers – The yield per acre of pepper is about 0.39 tonnes per hectare. This indicates a plant population of 10,250 plants per acre, thus the average yield per plant is 3.6 pounds.
Beetroot – The beetroot crop yields about 20–25 tonnes/hectare in 120 days.
Radishes – It yields about 200 to 250 quintals fresh radish per hectare.
Lettuce – The average yield of lettuce is about 80 to 120 quintals per hectare.
The above information may also be used for Polyhouse vegetable farming, Greenhouse vegetable farming, and even vegetable farming at home. In case if you are interested in this: How to Make Money from a Vegetable Farming .
10 COMMENTS
Thanks for ur information it’s very useful to me..
insightful information for beginners like me. How can I get this information handy for referral purposes during my start up farming carrer
I would like to set a agriculture business in 100 Acre land in Gujarat. I need prepare a business plan which should include crop name, it production detail per year and estimed income. I also need to have deails of other related investmenet like equipments, storage facility, labour cost , water cost , fertiliser cost etc
I want to be a farming business man
The content is important for a small scale farmer who is not in a position to get extension services from agricultural officers. It help me acquire some knowledge in writing a proposal for my vegetable project.
Good information for me to start my vegetable project to feed my country I would like to receive more information through my email as a guide for my project Thank you
Thanks for the Info, I am planning to start the farming can I get more info about the farming with Advance Technology how we built the prototype model first.
This is a great insight into vegetable farming. I wanna develop a business plan for vegetable production on campus. How can I start and what kind of marketing strategy plan do I have to implement
Thank you for the information. Also I would like to receive more information.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Fertilizer: The Essential Ingredient for Global Food Security and Profitable...
Common challenges in strawberry farming: a beginners guide, maximizing yield in ridge gourd farming: best practices and tips , sustainable agriculture with crfs (controlled release fertilizers): a game-changer for..., organic farming vs. natural farming (zbnf): key principles and differences, strawberry nursery establishment and management, modi vision for indian agriculture, government support and policies for zbnf in india, deworming schedule for sheep: a beginners guide, ultimate guide to beans farming in kenya: from planting to..., ultimate guide to natural vegetable farming, natural farming for sustainable livestock management, dairy farm technology in india: the future of dairy husbandry, comprehensive guide to organic farming in villages, modern sheep farming technology: the future of sheep husbandry, goat farming technology: the future of goat husbandry, how to build a low-budget goat shed: cheap ideas and..., goat farming training programs in india: a beginner’s guide, types of pesticides used in agriculture: a beginner’s guide, economical aquaculture: a guide to low-budget fish farming, borewell drilling cost, pump price, and pipe cost, polyhouse subsidy, cost, profit, project report, tractor subsidy, bank loan, eligibility, schemes, process, malabar neem project report details guide, cold storage project report, cost and subsidy, mushroom farming project report, cost and profit analysis.

Item added to your cart
Download all the resources to open a fruit and vegetable market.
Let's make sure your produce market will be profitable!
Business Model Canvas for a fruit and vegetable store (examples)
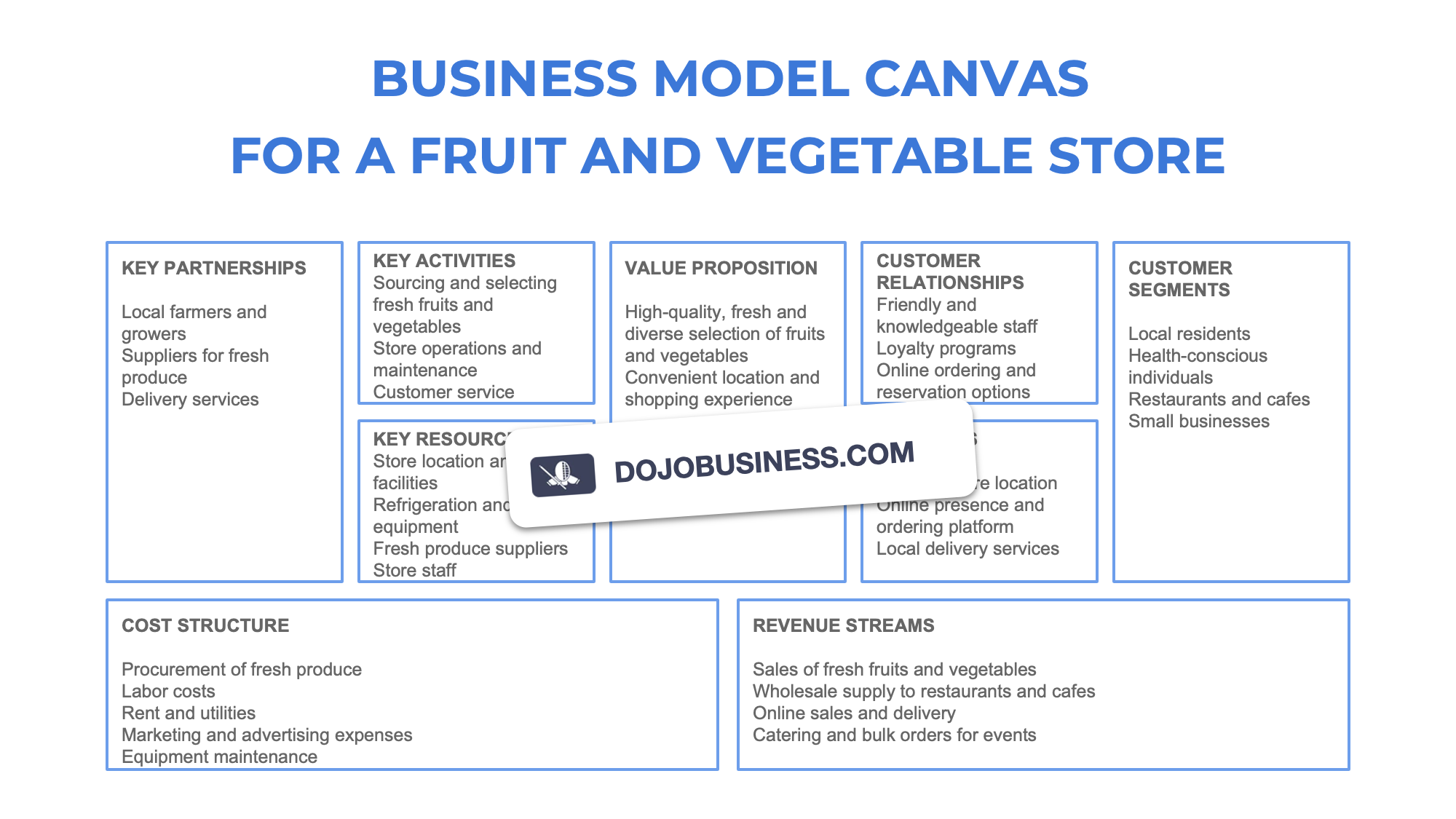
Get a watermark-free, fully customizable business model canvas in our business plan for a fruit and vegetable store
In the vibrant marketplace of fresh produce, having a clear and effective strategy is essential for your fruit and vegetable store to thrive.
Welcome to your detailed guide on applying the Business Model Canvas framework, customized for the unique needs of fruit and vegetable retailers.
This piece simplifies the framework into manageable sections, enabling you to pinpoint your value proposition, define your target customers, outline key operations, and much more.
Should you be looking for a ready-to-use Business Model Canvas that's fully customizable, feel free to explore our business plan template designed specifically for a fruit and vegetable store .
What is a Business Model Canvas? Should you make one for your fruit and vegetable store?
A Business Model Canvas is a strategic tool designed to help you map out the key components of your business, whether you're starting fresh or re-evaluating an existing business.
Imagine it as a visual framework that captures your fruit and vegetable store's value proposition, operations, customers, and financials in one succinct diagram.
In the context of a fruit and vegetable store, this canvas serves as a roadmap that illustrates how your store will generate revenue, attract and retain customers, and manage your resources effectively.
Why do people create a Business Model Canvas? It's simple. For owners of a fruit and vegetable store, the canvas offers a clear and concise picture of the business's core aspects. It helps you understand how you'll provide value to your customers, differentiate yourself from competitors, and maintain a profitable operation.
This might involve detailing your sources of fresh produce, your marketing tactics to attract health-conscious consumers, or your delivery services that set you apart from other stores.
The benefits are clear-cut.
It promotes strategic planning and helps you concentrate on the essentials. It can reveal unforeseen challenges or opportunities, allowing you to refine your approach before you invest too much time or money.
For example, you might discover that your plan to source exotic fruits isn't as viable as offering locally-grown, organic produce that appeals to your community's preferences. Such insights can be invaluable.
Should you create one if you're embarking on a new fruit and vegetable store venture? Definitely.
It's an essential part of the planning process that can steer your decisions and strategies. It enables you to communicate your vision to potential investors or partners in a clear and succinct manner. A well-thought-out Business Model Canvas, similar to the one you'll find in our business plan template tailored for a fruit and vegetable store , can transform a vague idea into a concept backed by a strategic market understanding.
Is it useful for you? Absolutely, especially if you aim to establish a clear direction for your store. It compels you to methodically work through your business model and assess the viability of your store concept.
Moreover, it's a dynamic document that you can modify as your store expands or as the market evolves.
How to create a Business Model Canvas for your fruit and vegetable store?
Creating a Business Model Canvas for your fruit and vegetable store should be straightforward.
You can simply adapt the one we have already created and filled in our business plan template designed for a fruit and vegetable store .
Need more details? Let's dive into each section of the canvas, and we'll guide you on how to complete it with ideas and strategies, using a clear and concise approach.
Value Proposition
Let's start with the Value Proposition.
This is the core of your fruit and vegetable store. What sets your store apart? Is it the locally-sourced produce, the organic selection, or perhaps the convenience and customer service?
Consider what will make customers prefer your store over others.
It could be your commitment to sustainability, the variety of exotic fruits and vegetables you offer, or the freshness guarantee you provide.
Customer Segments
Moving on to Customer Segments.
Who are your customers? Are you catering to health-conscious individuals, families looking for quality produce, or perhaps chefs and restaurants in need of premium ingredients?
Understanding your target audience will influence many of your choices, from product range to pricing policies.
Now, let's consider Channels.
How will you reach your customers? This might include a physical storefront complemented by online sales.
Think about leveraging social media to showcase your fresh produce, a website for online shopping and delivery options, and local advertising to engage the community.
Remember the importance of word-of-mouth and think about ways to motivate customers to refer friends and family.
Customer Relationships
Customer Relationships are about how you connect with your customers and ensure they return.
Outstanding customer service, rewards for regular shoppers, and responding to customer feedback are crucial.
Consider how you can use technology to improve the shopping experience, such as a loyalty app or online order tracking.

Revenue Streams
In the Revenue Streams section, you'll think about how your store will generate income.
Beyond direct sales, consider additional streams like offering subscription boxes, hosting educational workshops, or partnering with local businesses for produce supply.
Be innovative and think about what aligns with your brand and customer needs.
Key Activities
On the flip side, we have Key Activities.
These are the critical tasks required to run your store. This includes sourcing produce, managing stock, marketing, and customer service.
Identify the activities that are essential to delivering your value proposition and how you can perform them effectively.
Key Resources
Key Resources are the assets vital to your operation.
This includes your storage facilities, your staff, your relationships with farmers, and even your store's location. Reflect on what you need to succeed and how you can obtain these resources.
Key Partnerships
Key Partnerships might involve local farmers, organic certifiers, or collaborations with community organizations.
For example, partnering with a local composting service can help you manage waste and support community gardens.
Cost Structure
Finally, Cost Structure.
Operating a fruit and vegetable store comes with various expenses, from lease and employee wages to procurement and marketing costs. Understanding these will help you manage your finances effectively.
It's crucial to distinguish between fixed costs, like rent, and variable costs, like inventory, to budget wisely.
What should be included in each section of the Business Model Canvas for a fruit and vegetable store?
Unsure about how to tailor the Business Model Canvas for your fruit and vegetable store? You can start by modifying the template we've included in our business plan template .
Here's a guide with examples to help you fill out each section of the Business Model Canvas for a fruit and vegetable store.

Examples of Business Model Canvas for a fruit and vegetable store
Below are examples of business model canvas of three different types of fruit and vegetable stores: Organic Produce Store, Discount Produce Market, and Exotic Fruit Boutique.
Organic Produce Store Business Model Canvas
Discount produce market business model canvas, exotic fruit boutique business model canvas.

You can also read our articles about: - how to build a marketing strategy for your fruit and vegetable store - how to segment the customers of your fruit and vegetable store - how to make a competition study for your fruit and vegetable store - how to open a fruit and vegetable market (guide)
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.

How to Start Exotic Fruit Farming: Comprehensive Checklist for Beginners

Exotic Fruit Farming Bundle
Are you looking to venture into the exciting world of exotic fruit farming business? Look no further! In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through 9 essential steps to help you open, start, or launch your very own exotic fruit farm. Whether you're a novice farmer or seasoned entrepreneur, this checklist will provide you with the necessary tools and strategies to succeed in this lucrative industry.
According to recent statistics, the exotic fruit farming industry in the US is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for unique and healthy fruit options. As a result, more farmers are exploring the potential of growing exotic fruits to meet this rising market demand. By following our step-by-step checklist, you can position yourself for success and tap into this growing market effectively.
From creating a solid business plan to implementing a robust marketing strategy and continuous improvement practices, each step outlined in this checklist is designed to help you navigate the complexities of starting an exotic fruit farming business. So, roll up your sleeves, put on your farmer's hat, and get ready to embark on an exciting journey into the world of exotic fruits!
- Create a business plan.
- Conduct market research.
- Plan finances.
- Secure funding.
- Ensure legal compliance.
- Set up the farming operation.
- Select and plant crops.
- Implement marketing strategy.
- Focus on continuous improvement and expansion.
9-Steps To Start a Business
Business plan creation.
Developing a comprehensive business plan is the crucial first step in launching your Exotic Fruit Farming venture. Your business plan should outline your mission, vision, target market, operational strategy, marketing plan, and financial projections. This document will serve as a roadmap for your business and guide your decision-making process as you navigate the challenges of starting and growing your farm.
- Mission and Vision: Clearly define the purpose and goals of your Exotic Fruit Farming business. What sets you apart from competitors? What impact do you hope to have on your community and the environment?
- Target Market: Identify your ideal customer base. Are you targeting health-conscious consumers, foodies looking for unique flavors, or local restaurants and grocery stores? Understanding your target market will help shape your marketing strategies.
- Operational Strategy: Outline how you plan to run your farm on a day-to-day basis. This includes farm setup, equipment needs, staffing requirements, and crop management practices. Consider factors such as sustainability, organic certification, and technology integration.
- Marketing Plan: Develop a detailed marketing strategy to promote your Exotic Fruit Farming business and attract customers. This may include online and offline tactics such as social media marketing, farm tours, farmers' market participation, and partnerships with local businesses.
- Financial Projections: Create realistic financial projections for your Exotic Fruit Farming venture. Estimate your startup costs, operating expenses, revenue projections, and break-even point. Consider seeking the help of a financial advisor or accountant to ensure accuracy.
Tips for Business Plan Creation:
- Be specific and detailed in your business plan to provide a clear roadmap for success.
- Regularly review and update your business plan as your Exotic Fruit Farming business evolves and grows.
- Seek feedback from mentors, industry experts, and potential investors to strengthen your business plan.
Market Research
Before diving into the world of Exotic Fruit Farming business, it is crucial to conduct thorough market research to set a solid foundation for your venture. Market research will help you identify potential customers, understand market demand, assess competition, determine price points, and select the best exotic fruits to grow based on local climate and soil conditions.
Identifying Potential Customers: Start by understanding who your target customers are. Are they health-conscious individuals looking for nutritious fruits? Are they foodies interested in trying new exotic flavors? Knowing your target market will help you tailor your marketing strategies and product offerings accordingly.
Assessing Market Demand: Research the demand for exotic fruits in your local area. Are there any gaps in the market that you can fill with your unique produce? Look for trends in consumer preferences and behaviors to capitalize on opportunities in the market.
Understanding Competition: Study your competitors in the Exotic Fruit Farming industry. Analyze their strengths and weaknesses, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and customer base. This will help you differentiate your farm and develop a competitive edge in the market.
Selecting the Best Exotic Fruits: Consider the local climate and soil conditions when choosing which exotic fruits to grow on your farm. Some fruits may thrive in specific environments, while others may require more attention and care. Conduct research on the feasibility and profitability of growing certain fruits in your region.
Tips for Market Research:
- Utilize online surveys and focus groups to gather insights from potential customers.
- Attend farmers' markets and food festivals to observe consumer behavior and preferences firsthand.
- Collaborate with local chefs and restaurants to understand their needs and requirements for sourcing exotic fruits.
Financial Planning
Exotic Fruit Farming requires careful financial planning to ensure the success and sustainability of the business. Creating detailed financial models that include startup costs, ongoing operational expenses, projected revenue, and a break-even analysis is crucial for managing budgets and securing future funding.
Here are some key steps to follow in the financial planning process:
- Startup Costs: Identify all the initial expenses required to establish your Exotic Fruit Farming business. This may include land purchase or lease, farming equipment, infrastructure development, seedlings, labor costs, and legal fees.
- Ongoing Operational Expenses: Estimate the recurring costs involved in running your fruit farm on a day-to-day basis. This may include labor wages, utilities, maintenance, fertilizers, pest control, packaging materials, transportation, and marketing expenses.
- Projected Revenue: Conduct market research to determine the demand for exotic fruits in your target market. Based on this information, create realistic revenue projections for your Exotic Fruit Farming business. Consider different revenue streams such as direct sales, value-added products, and wholesale supply to restaurants and stores.
- Break-Even Analysis: Calculate the point at which your Exotic Fruit Farming business will cover all its costs and start making a profit. This analysis will help you set pricing strategies, determine production levels, and evaluate the viability of your business model.
Financial Planning Tips:
- Consult with financial advisors or agricultural economists to ensure your financial models are accurate and realistic.
- Regularly review and update your financial projections to reflect changes in market conditions, production costs, and revenue streams.
- Consider setting aside a contingency fund to cover unexpected expenses or revenue fluctuations.
Funding Acquisition
One of the key elements to starting an Exotic Fruit Farming business is securing the necessary funding to get your operations off the ground. There are various funding options available to entrepreneurs looking to enter the agriculture industry, including small business loans , grants , venture capital , and angel investors .
Before you begin the funding acquisition process, it is important to have a solid business plan in place that outlines your financial projections and funding needs. This will help you determine how much capital you need to raise and how you plan to utilize the funds to grow your Exotic Fruit Farming business.
Tips for Funding Acquisition:
- Research and identify the funding options that align with your business goals and financial needs.
- Prepare a compelling pitch that clearly articulates your business concept, market opportunity, and revenue potential to attract potential investors.
- Gather all necessary documents, including financial statements, business plans, and legal documents, to present a comprehensive funding proposal.
When approaching lenders or investors for funding, it is essential to be transparent and honest about your business and the risks involved. Building trust with potential funding sources is crucial to securing the capital you need to launch and grow your Exotic Fruit Farming venture.
Remember, securing funding is just the first step in building a successful Exotic Fruit Farming business. It is important to manage your finances prudently and use the capital wisely to achieve sustainable growth and profitability in the long run.
Legal Compliance
When establishing an Exotic Fruit Farming business, it is crucial to ensure that you obtain all necessary permits and licenses to operate legally. This includes various regulatory requirements that may vary depending on your location and the type of fruits you intend to cultivate.
Here are some key steps to help you navigate the legal compliance aspect of starting your Exotic Fruit Farming venture:
- Research Local Regulations: Begin by researching the specific regulations and requirements for fruit farming in your area. This may include zoning laws, land use permits, water rights, and environmental regulations.
- Obtain Land Use Permits: Depending on the size and scope of your farm, you may need to obtain land use permits from local authorities. These permits regulate the use of land for farming purposes.
- Secure Water Usage Rights: Water rights are essential for farming as they determine your access to water for irrigation. Ensure you have the necessary permits or licenses to use water for your Exotic Fruit Farming operations.
- Organic Certification: If you plan to grow organic fruits, consider obtaining organic certification. This certification verifies that your fruits are grown using organic farming practices and meet specific standards.
Tips for Legal Compliance in Exotic Fruit Farming:
- Consult with an Attorney: Seeking legal advice from an attorney specializing in agriculture can help you navigate the complex regulatory landscape and ensure compliance.
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed records of permits, licenses, and certifications to demonstrate compliance with legal requirements.
- Stay Updated: Stay informed about any changes in regulations or new requirements related to Exotic Fruit Farming to adapt your operations accordingly.
When starting an Exotic Fruit Farming business, choosing the right location for your farm is crucial to ensure the success of your operations. Consider factors such as climate, soil type, and water availability before making a decision. Here are the key steps to follow for setting up your farm:
- Research the climatic conditions that are suitable for the exotic fruits you plan to grow. Ensure that the location you choose offers the right temperature and humidity levels for optimal fruit production.
- Consider the soil type required for your chosen fruits. Some exotic fruits thrive in well-drained sandy soil, while others prefer loamy or clay soil. Conduct soil tests to determine the soil composition of potential locations.
- Availability of water is essential for fruit farming. Ensure that the location has access to a reliable water source for irrigation purposes. Consider the rainfall patterns in the area as well.
Tips for Selecting the Right Location:
- Consult with local agricultural extension services or agronomists for expert advice on suitable locations for exotic fruit farming.
- Visit potential locations multiple times during different seasons to observe how the climate and soil conditions vary throughout the year.
- Consider proximity to markets and distribution channels to reduce transportation costs and ensure fresh delivery of your fruits to customers.
- Determine the amount of land you will need based on the scale of your Exotic Fruit Farming operations. Consider factors such as crop rotation, expansion plans, and farming infrastructure requirements.
- Research local land prices and availability to find a suitable plot for your farm. Evaluate the soil quality, topography, and accessibility of the land before making a purchase or lease decision.
- Negotiate terms with landowners for lease agreements or secure financing for land purchase if required. Ensure that the land meets zoning regulations and permits for agricultural use.
- Identify the specific equipment and technology needed for efficient farming operations based on the size and scope of your Exotic Fruit Farming business. This may include tractors, irrigation systems, pruning tools, and harvesting equipment.
- Explore modern farming technologies such as precision agriculture tools, drones, and monitoring systems to optimize your farm productivity and resource management.
- Source equipment from reputable suppliers or consider leasing options to reduce upfront costs. Invest in training for yourself and your farm workers to ensure proper use and maintenance of the equipment.
Crop Selection And Planting
Choosing the right exotic fruits to grow on your Exotic Fruit Farming business is a crucial step that can determine the success of your venture. Conduct thorough market research to identify the demand for different exotic fruits in your target market. Consider factors such as taste preferences, trends, and the availability of similar fruits in the market.
Additionally, take into account the climatic conditions of your region when selecting the crops to cultivate. Different exotic fruits thrive in varying environments, so it is essential to choose fruits that are well-suited to your specific climate.
Once you have identified the suitable exotic fruits to grow, begin the planting process by sourcing quality seeds or saplings from reputable suppliers. Ensure that the seeds or saplings are healthy and disease-free to set a strong foundation for your crop.
When planting the exotic fruits, pay attention to proper spacing between plants to allow for adequate growth and airflow. Proper spacing can help prevent diseases and maximize the yield of your crops.
Soil management is another critical aspect of the planting process. Conduct soil tests to determine the nutrient levels and pH of your soil. Based on the results, make any necessary amendments to ensure that your exotic fruits have access to the nutrients they need for healthy growth.
Tips for Crop Selection and Planting:
- Diversify your crop selection: Consider growing a variety of exotic fruits to appeal to a wider customer base and reduce the risk of crop failure.
- Consult with experts: Seek advice from agricultural extension services or experienced farmers to gain insights into the best practices for planting exotic fruits.
- Stay updated on industry trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in the exotic fruit market to make informed decisions on crop selection and planting.
Marketing Strategy Implementation
Developing and implementing a comprehensive marketing strategy is essential for the success of your Exotic Fruit Farming business. This strategy should encompass various elements such as branding, online presence, partnerships with local markets, and promotional events to educate consumers about the unique qualities of your fruits.
Branding: Establishing a strong brand identity is crucial for setting your Exotic Fruit Farming business apart from competitors. Consider creating a logo, choosing a color scheme that reflects the essence of your fruits, and developing a unique selling proposition that resonates with your target market.
Online Presence: In today's digital age, having a strong online presence is non-negotiable. Create a professional website that showcases your Exotic Fruit Farming products, provides information about your farm and practices, and enables customers to place orders online. Additionally, leverage social media platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter to engage with your audience and share updates about your fruits and farm.
Partnerships with Local Markets: Collaborating with local farmers' markets, grocery stores, and restaurants can help you reach a wider audience and increase sales. Consider forming partnerships with establishments that align with your brand values and target demographics to maximize exposure for your Exotic Fruit Farming business.
Promotional Events: Organizing promotional events such as fruit tastings, farm tours, and workshops can help educate consumers about the unique qualities of your fruits and generate buzz around your Exotic Fruit Farming business. Consider partnering with local influencers, food bloggers, or media outlets to amplify the reach of your events and attract new customers.
Tips for Effective Marketing Strategy Implementation:
- Engage with your audience on social media by sharing behind-the-scenes glimpses of your farm and products.
- Collaborate with local food bloggers or influencers to increase visibility and reach a wider audience.
- Offer special promotions or discounts to incentivize first-time customers and encourage repeat purchases.
Continuous Improvement And Expansion
As you establish your Exotic Fruit Farming business, it's essential to prioritize continuous improvement and expansion to stay competitive in the market. Regularly reviewing your business performance against set goals and being prepared to make adjustments is crucial for long-term success.
Explore Opportunities For Expansion: One way to expand your Exotic Fruit Farming business is by increasing your product offerings. Consider introducing new exotic fruits to attract a wider customer base and keep your offerings fresh and exciting. Additionally, you can explore the option of offering additional farm tours to educate customers about your farming practices and create a unique experience for them.
Extend Your Distribution Network: Another avenue for expansion is to extend your distribution network to include more local restaurants and stores. By partnering with these establishments, you can increase your reach and make your exotic fruits more accessible to a larger audience. This can also help you generate additional revenue streams and build valuable relationships within the community.
Tips for Continuous Improvement and Expansion:
- Regularly solicit feedback from customers to understand their preferences and improve your products and services.
- Stay updated on market trends and consumer demand to anticipate future opportunities for growth.
- Invest in technology and farming practices that can help increase efficiency and productivity on your farm.
Starting an exotic fruit farming business requires careful planning, research, and execution. By following the 9 steps outlined in this checklist, you can set yourself up for success in the industry. From developing a solid business plan to selecting the right crops, implementing a marketing strategy, and continuously improving your operations, each step is crucial for the long-term success of your venture.
- Creating a comprehensive business plan
- Conducting thorough market research
- Developing detailed financial models
- Exploring funding options
- Ensuring legal compliance
- Selecting an appropriate location and setting up your farm
- Choosing the right crops and planting them correctly
- Implementing a robust marketing strategy
- Continuously improving and expanding your business
By following this checklist and staying committed to your goals, you can establish a thriving exotic fruit farming business and contribute to the growing demand for unique and healthy fruits in the market.
Related Blogs
- Exotic Fruit Farming Business Idea Description in 5 W’s and 1 H Format
- Exotic Fruit Farming Owner Earnings: A Comprehensive Guide
- 7 Key Metrics for Monitoring Exotic Fruit Farming
- What Are the Major Expenses in Exotic Fruit Farming?
- How to Maximize Profits on Your Exotic Fruit Farm
- Essential Startup Costs For Your Exotic Fruit Farm
- How to Create a Business Plan for Exotic Fruit Farming: Tips for Success
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Produce Farm Business Plan
Start your own produce farm business plan
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens (MGSG) is an exciting new company that meets an unsatiated need for quality salad greens. The close proximity to Eugene ensures a steady flow of customers. MGSG is a start-up grower and distributor of exotic salad greens for restaurants and individual consumers. MGSG is located in Blue River, Oregon and serves the southern Willamette Valley. MGSG’s objectives are to develop a product-based company whose goal is to exceed customer’s expectations, increase production efficiency by 10% a year, and lastly, and develop a sustainable farm business, able to survive off their cash flow.
MGSG will sell a spring mix of salad field greens. These greens will include but are not limited to: red leaf, arugula, radicchio, mustard greens, endive, and chicory. These greens are grown for use in salad mixtures, purchased by the end consumer as well as by restaurants who then serve it to their patrons.
MGSG has decided to target two distinct market segments, individual customers and restaurants. The individual customers will purchase greens from MGSG at the Tuesday and Saturday Farmer’s Market. This segment is growing at 12% and has 12,000 potential customers. The second segment is local restaurants. This market is smaller at only 28 potential customers, but is more consistent in demand throughout the year.
Competitive Edge
MGSG has two competitive edges that will help them maintain strong growth rates, increasing their market penetration. The first edge is quality. MGSG prides themselves on the high quality of exotic salad greens. Greens that do not meet MGSG high standards of quality are rejected as imperfects and go to a not-for-profit food bank. MGSG’s second competitive edge is their flexibility. The entire farm has been set up to allow them to change crops or scale existing crops to meet demand. This is highly unusual as most farms are unable to change crops mid year.
MGSG is led by Heidi Ponic. Heidi initially got her start in growing while working at a greenhouse. After college, Heidi went to work for a large grass seed company. This experience is what solidified Heidi’s desire to continue working in an agricultural capacity. Soon after her experience at the Willamette Seed Company she decided to enroll in Oregon State University’s Master of Horticulture Program. Heidi’s Masters provided her with requisite detail and skills to develop her own farm business.
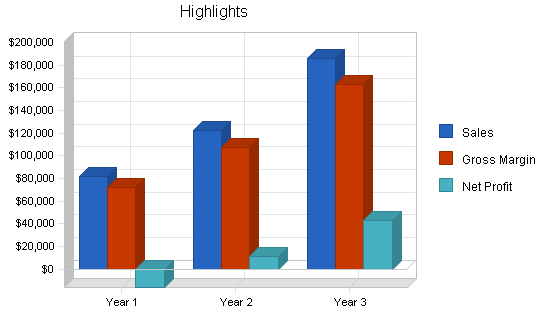
1.1 Objectives
The objectives for the first three years of operation include:
- To create a product-based company whose goal is to exceed customers’ expectations.
- To increase the efficiency of our production by 10% a year.
- To develop a sustainable farm, surviving off its own cash flow.
1.2 Mission
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ mission is to provide the highest-quality salad greens. We exist to attract and maintain customers. When we adhere to this maxim, everything else will fall in to place. Our services will exceed the expectations of our customers.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens, soon to be located in Blue River, OR, is a grower and seller of exotic salad field greens. MGSG grows a wide variety of field greens including red leaf, arugula, radicchio, mustard greens, endive, and chicory. MGSG sells the greens both at farmer markets as well as direct to restaurants.
The business will be based out of Heidi Ponic’s home. The office will be within her home and the greenhouse will be on her adjoining 20 acres of land.
2.1 Company Ownership
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens will be a sole proprietorship with Heidi Ponic as the founder and owner. Heidi will be funding the business with a $50,000 investment of her own. An additional $10,000 will be invested by family member O.G. Tylthe with exit/repayment initially scheduled for year five.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ start-up costs will include all the equipment needed for the home-based office, the construction of the greenhouse and all the necessary equipment, and other essentials for growing.
The home office equipment will be the largest chunk of the start-up expenses. This equipment includes a computer system, fax machine, office supplies, cellular phone, and pager. The computer should have at least a 500 megahertz Celeron/Pentium processor, 64 megabytes of RAM (preferably 128), 6 gigabyte hard drive, and a rewritable CD-ROM for backing up the system. The home office will also require a few pieces of furniture such as a desk, chair, and book shelf to transform a standard room into an office. Lastly, an additional land phone line will be required.
The greenhouse will need the following equipment: a 25′ x 100′ greenhouse structure made out of poly carbonate, a ventilation system, a heater, a mister system, supplemental lighting, fertilizer injector, pruners, pots, trays, soil, seeds, and assorted chemicals.
Please note that of the $25,300 of long-term assets, $20,000 will be depreciated straight line for 27.5 years (real estate) and the remaining $5,300 will be depreciated on a seven year straight-line schedule.
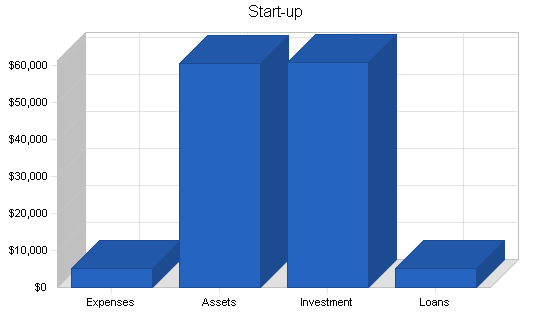
MGSG will sell a spring mix of salad field greens. These greens will include but are not limited to: red leaf, arugula, radicchio, mustard greens, endive, and chicory. These greens are grown for use in salad mixtures, purchased by the end consumer as well as by restaurants who then serve it to their patrons. While the greens are washed at the farm, they are not certified washed and the patrons are told to wash them an additional time.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
MGSG will be focusing on two distinct users of greens, individual consumers, and restaurants. The consumer market is seasonal so we will have production shifts during the consumer off season and all of the production will go toward wholesale restaurant distribution. During the spring and the summer MGSG will be serving both the consumer markets through farmer market stands and the restaurants through direct distribution.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens has two distinct customers:
- Individual Consumers . This group of people buy exotic salad greens because they have a more sophisticated pallette. Average Americans have been raised on iceberg lettuce and this is their green of choice (unfortunately). When people from this class get a little “crazy” they might even try romaine lettuce. These people are typically unsophisticated or unadventurous in terms of culinary habits. These are NOT the people MGSG serves. MGSG is going after people that appreciate healthier, tastier alternatives to the standby of iceberg lettuce. This group of consumers is more likely to make their own meals instead of going out, appreciates fine dining, and generally is from a higher socio/economic class. Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ field greens are more expensive than choices like iceberg or romaine, therefore one can conclude that the consumer typically makes more money if they are willing to pay significantly more for their salad greens, and second, people with more sophisticated palates typically are more educated.

- Restaurants . Not all restaurants use exotic field greens mixes, generally it is a restaurant of fine dining that serves the finer greens. To be even more specific, it is typically an adventurous American or nouveau cuisine restaurant as opposed to a nicer French or German restaurant that appreciates the exotic field greens mix. For what ever reason (probably attributable to demand of their customers), the French and German restaurants, even the finer ones tend to serve “peasant greens.” The restaurants are a year round customer which is helpful to balance the seasonal demand of individual consumers (group 1 above). Another advantage of having the restaurants as a customer is that even though they get a better price, MGSG has a long term contract with them which helps out in terms of stability.

4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ target market segment strategy is fairly easy. Our two different customer groups purchase from two distinct locations so it is quite easy to target them individually.
Individuals . These customers will be buying MGSG products from the different farmer markets located in Eugene, OR. The main one is “The Farmers Market” held downtown twice a week in the spring, summer, and the early autumn. This market gets quite a bit of traffic because there is a nice selection of different farmers and products and it is in a central location in the heart of Eugene. Additionally, there are several other smaller farmer markets that exist in outlining communities. By setting up a booth in these markets, there is already a steady flow of interested customers. There obviously is a fee to set up a stand, but what you get for the fee is all of your marketing taken care of and a line of customers. In addition to individuals frequenting the farmer markets, some restaurants will go there as well. This occurs when a restaurant needs certain ingredients but did not have the time to order it in advance.
Restaurants . MGSG will target these customers by introducing MGSG and their products to the restaurants through meetings with the buyers at each restaurant. There are about 25-30 different restaurants in Eugene that use field greens in their salad and MGSG intends to approach these to form long-term relationships.
4.3 Industry Analysis
There are three different types of competitors that MGSG faces:
- Supermarkets . These stores sell a salad greens mix to consumers. The advantage of the supermarket is convenience. There are many supermarkets around the city and they are open many hours during the day. Their disadvantage is price and quality. The quality and variety lower than the standards set by the offerings of MGSG and other similar local farmers. The cost is higher, usually 15% more.
- Similar local farmers . These are very similar operations to MGSG, sometimes larger and sometimes smaller. There appears to be room in the market for multiple farmers as most of the farmers sell out their products each day at the farmer markets.
- Large distributors . An example of this would be Food Service of America (FSA) which buys a wide variety of products and quality of produce from farmers and distributes them to restaurants. The produce is not usually local, and is a few more days older from the field compared with the local farmers. The price is comparable and the quality can be comparable, but not necessarily. The disadvantage of a food distributor is the lack of flexibility relative to a local grower when serving local customers.
Buying patterns are based on the customer’s desires. What is meant by this is that lower-end restaurants (or at least restaurants that are less concerned about quality) will not bother to get greens from local farmers, there is no need for them to. This pattern is similar for the individuals. There are some individuals that are content with the offerings from supermarkets. There are others that appreciate the difference in quality and are willing to schedule a trip to the farmers market to meet their weekly needs.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
MGSG will be aggressively courting the farmer markets to ensure the ability to have a booth at the markets. Additionally, MGSG will be aggressive in going after the local restaurants that have a consistent need for the greens. Through an assurance of top-shelf service and superior customer service and reliability, MGSG will continue to grow its number of clients.
5.1 Competitive Edge
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ competitive edge has two main aspects: quality and flexibility.
- Quality . While the quality of the other local farmers is quite good, Heidi’s extensive educational background and practical experience provides her with tools to create a superior product. Heidi is a perfectionist and her striving for perfection will lead MGSG to developing a product that will be a notch better than the competition.
- Flexibility . With MGSG being both small and local in nature, it will be able to be flexible in meeting customer’s demands. For instance, if a local restaurant has customers that prefer more arugula in their salad mix, MGSG can rapidly shift production to meet the needs of that customer. Most of the farmers, and all of the distributors, typically have their production schedules set up for maximum yield and are unable to modify crop production very much. Heidi is less concerned about maximizing yield, she is more concerned with pleasing the customer. She believes, rightfully so, that talking care of the customer is the most important thing.
A combination of quality and flexibility will create a sustainable competitive advantage that will allow MGSG to succeed.
5.2 Sales Strategy
MGSG’s sales strategy will be based on visibility, consistency, and strategic relationships.
- Visibility . MGSG will need to generate visibility that sets them apart from the other local farmers that sell at the market. This in part will be done through the use of a colorful, distinct booth set-up that stands out among the other farmers. This visibility will create recognition for MGSG. This is important because the produce of the different farmers appears to be the same. The differences are discovered upon tasting the produce in your home. If MGSG stands out in terms of the booth appearance, the repeat customer will more easily make the connection between the unusual booth and MGSG’s product.
- Consistency . In addition to product consistency, MGSG will have consistency in regards to their presence at the farmer markets. It is much easier to build awareness and loyalty if people can reliably expect to see MGSG every week in the same place.
- Strategic relationships . This will be the key for restaurant sales. As stated before, restaurant sales are a consistent income that help reduce the seasonality of MGSG’s sales. Forming mutually beneficial, strategic partnership will be of upmost importance for building a good revenue base.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast

5.3 Milestones
MGSG will have several milestones early on:
- The end of the consumer season and the ramping up of the restaurant supply cycle.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Heidi Ponic, founder and owner, first became interested in growing vegetables at the age of five. Heidi pursued her love for plants by obtaining a biology degree at the University of Washington. Throughout her last three years at Washington, she worked in a greenhouse that grew many different types of annuals. Upon graduation, Heidi went to work for a large grass seed manufacturer. Although the growing of grass seed proved to be far less interesting then most other plants, she was determined to get management experience, a skill set that she lacked. After two years at Willamette Seed Company, she enrolled in Oregon State University’s Masters of Horticulture program.
Having gone through the three years of the Masters program, she realized two things, 1) she needed to create a job/company for herself, 2) she should follow her passion and grow vegetables. These realizations were the final catalyst to pursue her lifelong dream of running her own greenhouse operation.
Heidi’s educational training and her passion creates the ideal combination for an owner of a start-up company.
6.1 Personnel Plan
The staff will consist of Heidi working full time. While the bulk of the time Heidi will spend managing the operation, she will always spend a few hours a week tending to the plants. In addition to all of the general management required for the production of the greens, Heidi will be setting up strategic relationships with local restaurants. Mixed Greens Salad Gardens will have hired two full-time gardeners beginning in the middle of the first month, and will hire a part-time helper by month four. The gardeners will be primarily responsible for the raising of the field greens, while the part-time help will be used to help staff the farmers market booth for the consumer selling of the greens.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline the important financial information.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The following table highlights some of the important financial assumptions.
7.2 Break-even Analysis
The Break-even Analysis below indicates the monthly sales needed to break even.

7.3 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table will indicate projected profit and loss. Our losses at start-up are evident, as is the turn of the corner in July when we become profitable.

7.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table will indicate projected cash flow.

7.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table will indicate the projected balance sheet.
7.6 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 0161, Lettuce Farms, as part of Vegetables and Melons, Not Elsewhere Classified, are shown for comparison.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Venturing into the world of exotic fruit farming requires meticulous planning and preparation. Before embarking on this journey, it's crucial to assess market demand, identify suitable land, and evaluate the necessary infrastructure and resources.From navigating regulatory requirements to building a network of suppliers and customers, this comprehensive 9-step checklist will guide you through ...
A good business plan for a fruit and vegetable market must cater to the unique aspects of this type of retail business. Initially, it's crucial to provide a comprehensive overview of the market landscape. ... We provide a wide array of fruits and vegetables, including rare and exotic items, to cater to the diverse tastes and needs of our customers.
Below is a sample vegetable farming business plan template that can help you to successfully write your own with little or no difficulty. A Sample Vegetable Farming Business Plan Template 1. Industry Overview. Vegetable farmers grow a wide variety of vegetables in open fields and in greenhouses. Some vegetable farmers also grow a variety of ...
The Value of Vegetable Farming Market. The vegetable farming market is large and diverse, with various segments and niches. According to a report by The Business Research Company, the global vegetable farming industry market is expected to grow from $1.65 trillion in 2023 to $1.76 trillion in 2024 at a CAGR of 6.5%. It's projected to reach $2.17 trillion in 2028 at a CAGR of 5.4%.
Soil preparation and management - Soil preparation and management for vegetable growing involves many of the usual operations required for other crops. Good drainage is important for early vegetables because of wet soil retards development. Propagation - Propagation of vegetable plants, involving the formation and development of new individuals in the establishment of new plantings, is ...
Specializes in rare and exotic fruits and vegetables from around the world, providing a unique shopping experience. Adventurous eaters, culinary enthusiasts. ... While the structure of a fruit and vegetable market business plan shares commonalities with other business plans, the focus on certain areas may vary. ...
Get a watermark-free, fully customizable business model canvas in our business plan for a fruit and vegetable store. ... For example, you might discover that your plan to source exotic fruits isn't as viable as offering locally-grown, organic produce that appeals to your community's preferences. Such insights can be invaluable.
Embarking on a venture in urban farming requires meticulous planning and preparation. Before crafting a comprehensive business plan, there are 9 crucial steps to consider. From conducting thorough market research to assembling a skilled team, this checklist ensures your urban farming endeavor is feasible, sustainable, and poised for success.Whether you're exploring vertical farming or seeking ...
Business Plan Creation. Developing a comprehensive business plan is the crucial first step in launching your Exotic Fruit Farming venture. Your business plan should outline your mission, vision, target market, operational strategy, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Explore a real-world produce farm business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. ... MGSG is a start-up grower and distributor of exotic salad greens for restaurants and individual consumers. MGSG is located in Blue River, Oregon and serves the southern Willamette Valley ...